Getting rid of the plum moth
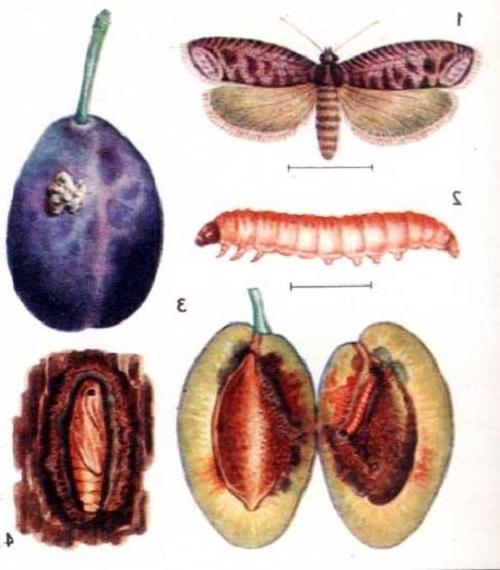
 Every gardener, having seen a seemingly harmless gray butterfly with brown spots on its wings on his plums, immediately begins to actively prepare to fight for his harvest. This nondescript insect called the plum moth is capable of completely depriving the crop not only in the current season, but also next year.
Every gardener, having seen a seemingly harmless gray butterfly with brown spots on its wings on his plums, immediately begins to actively prepare to fight for his harvest. This nondescript insect called the plum moth is capable of completely depriving the crop not only in the current season, but also next year.
The butterfly itself does not eat plums, but it lays eggs in them, from which caterpillars hatch after 10 days. So they just represent the main danger to the garden, literally eating up the crop.
The advantages and disadvantages of the biological method
One of the safest ways to get rid of pests is to use biological products that contain bacteria, viruses, fungi, or biopesticides. By the time the time comes to pick the plums, there will be no harmful substances in the fruits.
The following tools have proven themselves well:
- Iskra-Bio;
- Fitoferm.
Of the disadvantages of this method, it is worth noting that biological products are washed off, so in a rainy summer, trees will have to be processed several times.
Chemical method for the destruction of the moth
Treatment with insecticides, although it is a more dangerous method for humans, however, guarantees complete disposal of the pest. If the trees are processed on time and correctly, by the time of harvest, there will also be no hazardous substances in the fruits.
Of the chemical preparations against the moth, the following insecticides can be used:
- Kinmix;
- Alatar;
- Decis.
In total, two treatments need to be carried out: after flowering (around the beginning of June), and one more - a month later (at the beginning of July).
If after a chemical attack there are still pests, they are already "finished off" with biological preparations, having processed the tree a month later (in early August).
Preventive measures
Caterpillars of the moth do not disdain other crops and happily eat apricots, pears, cherries and other fruits growing in the garden. To prevent the spread of pests throughout the garden, as well as to destroy the enemy at an early stage, the following methods are used:
- all fallen fruits must be picked up, burned or buried, the same applies to leaves;
- to clean off the bark lagging on the trunks, under which caterpillars can winter;
- put on trunks trapping adhesive belts for catching the moth;
- attract insectivorous birds to the garden by equipping them with feeders;
- loosen the trunk circle every 10 days to avoid the transfer of pests to other trees.
Of the folk methods, trees are sprinkled with ash and soap or herbal infusions (chamomile, potato tops, spurge).