How to independently calculate the optimal angle of inclination of the roof of a private house
 The angle of inclination of the roof is the most important parameter when erecting a rafter system and calculating the consumption of roofing materials for a private house. Roof design is a very responsible event that should be entrusted exclusively to professionals who have permission to carry out such work. However, in some cases, all preliminary calculations can be done independently, at least in order to have an idea of the expected amount of material and the possibility of implementing your architectural ideas. From this publication you will find out what it depends on and how to calculate the angle of inclination of the roof on your own, without resorting to the services of expensive specialists.
The angle of inclination of the roof is the most important parameter when erecting a rafter system and calculating the consumption of roofing materials for a private house. Roof design is a very responsible event that should be entrusted exclusively to professionals who have permission to carry out such work. However, in some cases, all preliminary calculations can be done independently, at least in order to have an idea of the expected amount of material and the possibility of implementing your architectural ideas. From this publication you will find out what it depends on and how to calculate the angle of inclination of the roof on your own, without resorting to the services of expensive specialists.
What affects the slope of the roof
All this does not mean at all that shallow roofs are better. On roofs with a low slope, the snow will linger longer, which creates an impressive load on the rafter system. In addition, the angle of the roof slope affects the dimensions of the attic space. The steeper the roof, the more opportunities the developer has for arranging a residential attic. However, one should not forget about the high cost of structures with steep slopes, especially in comparison with flat roofs. To save the volume of the attic space without increasing the height of the ridge, creating a sloping roof will help.
In addition to snow and wind loads, the weight of the roofing cake together with the weight of the rafter system also affects the frame. If insulating materials are used in the roof, then their weight is taken into account when determining the optimal roof angle.
How is the angle of inclination of the roof measured?
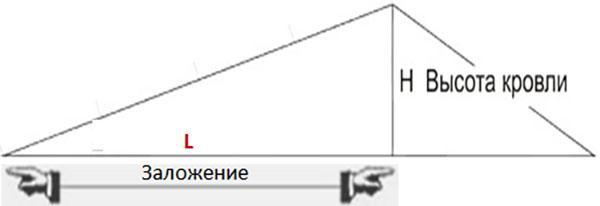 First of all, you should clarify the very concept of the angle of inclination. This value is the angle that is formed when the horizontal plane (laying) intersects with the roof plane. "Laying" is nothing more than a projection of the roof slope in a horizontal plane.
First of all, you should clarify the very concept of the angle of inclination. This value is the angle that is formed when the horizontal plane (laying) intersects with the roof plane. "Laying" is nothing more than a projection of the roof slope in a horizontal plane.
Reference books and specialized tables use percentages as the unit for measuring the angle of inclination of the roof. The roof slope as a percentage shows the ratio of the height of the roof (H) to the foundation (L).
In gable roofs (L) is a value equal to the length of half the span. L in pitched roofs is equal to the span length.
Rules for calculating the angle of inclination of the roof
 Let's say L = 3 m, and H = 1 m. In this case, the ratio will look like H to L or 1: 3. This is the simplest example, showing the great inconvenience in determining the slope angle in this way.
Let's say L = 3 m, and H = 1 m. In this case, the ratio will look like H to L or 1: 3. This is the simplest example, showing the great inconvenience in determining the slope angle in this way.
For simplicity of calculations, a special formula for calculating the angle of inclination of the roof is used, which looks like this.
I = H / L where:
- I is the slope of the slope;
- H - the height of the roof;
- L is the positioning value.
Let's use the data from the example above. L = 3 m and H = 1 m. Then, the calculation formula looks like I = 1/3 = 0.33.Now, to convert the tangent of an acute angle to a percentage, you need to multiply the resulting value by 100. Based on this, we get: 0.33 x 100 = 33%
How to determine the angle of inclination of the roof in degrees? There are two simple ways to convert percentages to degrees:
- use an online converter;
- use tables published in specialized reference literature.
The first method is quite simple, but requires an internet connection. The network contains a huge number of resources that provide an opportunity to use an online converter.
Roof slope tables in degrees and percentages are more difficult to find, but easier to use. We publish a table of the percentage-degree ratio.
Determine the minimum roof slope angle depending on the roofing material

Based on the steepness of the slopes, all roofs are conventionally divided into four types:
- High, with a slope from 45 to 60 °.
- Pitched, with a roof slope from 30 to 45 °.
- Gentle. The angle of inclination of the slopes in such structures varies from 10 to 30 °.
- Flat with a slope up to 10 °.
When approaching the construction of a roof, the developer plans to use a certain roofing material. It should be borne in mind that not every material can be used on roofs with different slopes.
Next, consider the relationship between the most common roofing materials and the minimum permissible roof slope angle:
- Asbestos-cement slate - 9 ° or 16%. The ratio of the height of the roof to the laying is 1: 6.
- Ondulin - 5 °. The aspect ratio is 1:11.
- The minimum angle of inclination of a single-pitched metal roof is 14 °.
- Ceramic tiles - 11 °. The ratio is 1: 6.
- Cement-sand tiles - 34 ° or 67%. The ratio of the height of the roof to the laying is 1: 1.5.
- Bituminous shingles - 11 °. Aspect ratio 1: 5.
- Corrugated board - 12 ° At a lower slope, it is necessary to process the joints with a sealing agent.
- Galvanized and steel sheets require a minimum slope of 17 °.
- Rolled bituminous materials - 3 °.
- The weld-on roof can be used as a roof covering with a 15% slope.
In the design of roofs, there is a concept - the maximum angle of inclination of the slopes. This value is critical for the use of a particular material. The figure below shows the minimum and maximum roof pitch angles for some common roofing materials. In addition, the last column contains data on which slope of the slope is most often used for these materials by domestic developers.
As you can see from the above table, there is a very substantial gap between the minimum and maximum angle of inclination of the roof.
When choosing a slope from the range of acceptable values, you should be guided solely by aesthetic considerations and material consumption.
Snow and wind loads
When designing a roof, snow and wind loads on the rafter system are always taken into account. The steeper the slopes, the less snow will linger on them.
To correctly calculate the required structural strength, a correction factor is introduced:
- For roofs with a slope of less than 25 °, a factor of 1 is applied.
- Roof structures with ramps from 25 to 60 ° require a factor of 0.7.
- Roofs made with a slope angle of more than 60 ° do not require the use of a coefficient, since snow practically does not linger on them.
For simplicity of calculations, maps are used in which the average values of snow load in the regions of the Russian Federation are marked.
Calculation examples
The calculation rules are simple: we find our region, determine the snow load, highlighted in our own color, take into account the first value, multiply by the correction factor based on the assumed angle of the roof slope. As an illustrative example, let's calculate the snow load for the roof of a house in Norilsk with a slope angle of 35 °. So, 560 kg / m2 multiply by a factor of 0.7.We get a snow load for a given region and a specific roof structure 392 kg / m2.
To determine wind loads, maps are also used, in which the calculated values of wind loads by region are marked.
In addition, the calculations should take into account:
- The wind rose, and specifically - the location of the house on the ground and in relation to other buildings.
- The height of the building.
According to the type of location of the house on the ground, all buildings can be divided into three groups:
- A - buildings located in an open area.
- B - Buildings located in settlements with a wind barrier not higher than 10 m.
- B - buildings located in settlements with a wind barrier from 25 m.
Depending on the area of placement and the height of the building, when designing the roof, correction factors are introduced taking into account the wind load. All factors influencing the wind load are summarized in a table for easy calculation.
For example: for a one-story house in Norilsk, the wind load will be: 84 kg / m2 multiplied by the factor 0.5 corresponding to zone "B", which is 42 kg / m2.
In addition, aerodynamic loads affecting the rafter system and roofing material are taken into account. Depending on the direction of the wind, the load is conventionally divided into zones, which assume different correction factors.
To ensure a safety factor, it is recommended to take values from the most loaded zones G and H.