Diseases of carrots and the fight against them
 Improper care of the carrot bed and non-observance of the rules of crop rotation can lead to the development of various diseases on the fruits of carrots. To start an active struggle and come out of it as a winner, you need to know the cause of the disease, the name and how to eliminate it.
Improper care of the carrot bed and non-observance of the rules of crop rotation can lead to the development of various diseases on the fruits of carrots. To start an active struggle and come out of it as a winner, you need to know the cause of the disease, the name and how to eliminate it.
The most common diseases
Phomoz, or dry rot
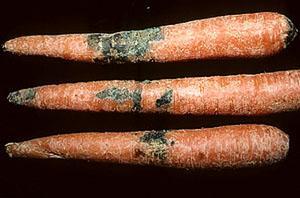
White rot or sclerotinia in carrots
 On the surface of root crops, a white coating is formed from thin hyphae of the fungus. The root crop retains its color, softens, later black dots of sclerotia and droplets of liquid appear. The disease turns the root crop into a pulp, spreads to neighboring vegetables. In addition to carrots, the fungus also affects other garden crops.
On the surface of root crops, a white coating is formed from thin hyphae of the fungus. The root crop retains its color, softens, later black dots of sclerotia and droplets of liquid appear. The disease turns the root crop into a pulp, spreads to neighboring vegetables. In addition to carrots, the fungus also affects other garden crops.
Gray rot (kagatny rot, botridiosis)
 Affects root crops during storage. Root crops are covered with a gray fungus, droplets of yellowish liquid are visible. The tissue of the vegetable turns brown, softens, soaks. The disease is nonspecific, it affects many vegetables, fruits, berries, not only carrots.
Affects root crops during storage. Root crops are covered with a gray fungus, droplets of yellowish liquid are visible. The tissue of the vegetable turns brown, softens, soaks. The disease is nonspecific, it affects many vegetables, fruits, berries, not only carrots.
Brown leaf spot
 At the soil level, the constrictions on the petioles are brown; seedlings often die. On adult plants, there are brown spots on the leaves with a dark rim. In the future, the leaves are curled. On root crops, the disease manifests itself in small, up to 1.5 cm, light brown spots. A sharp border between the affected and healthy tissue is characteristic.
At the soil level, the constrictions on the petioles are brown; seedlings often die. On adult plants, there are brown spots on the leaves with a dark rim. In the future, the leaves are curled. On root crops, the disease manifests itself in small, up to 1.5 cm, light brown spots. A sharp border between the affected and healthy tissue is characteristic.
Black rot or alternaria
On seedlings, the disease of carrots resembles a black leg - a black constriction, and a strong defeat in the early stages often leads to death. The defeat of adult plants is manifested in the darkening and curling of the tips of the leaves. In the future, spots of yellowish color appear, gradually the leaves drop and dry out. On root crops it is expressed by black dry rot.
Powdery mildew
 Any part of the plant, where the fungus has penetrated, is affected, the leaves turn white, harden, crumble. An idea of the appearance of this illness carrot gives a name, quite accurate. The fungus affects many garden crops. The plant does not die, but the root crop is formed small, sinewy.
Any part of the plant, where the fungus has penetrated, is affected, the leaves turn white, harden, crumble. An idea of the appearance of this illness carrot gives a name, quite accurate. The fungus affects many garden crops. The plant does not die, but the root crop is formed small, sinewy.
Bacteriosis, or wet rot
 The leaves turn yellow, then turn brown. At first, the extreme, lower parts of the leaf are affected. Between the brown and still green parts of the leaves there is a transitional yellowed zone. In the future, the petioles are captured, the leaves dry out. The defeat of root crops begins more often from the top or tip, as places are easier to injure. The spots grow, get wet, acquire an unpleasant odor. This disease is often carried by carrot fly larvae or other pests.
The leaves turn yellow, then turn brown. At first, the extreme, lower parts of the leaf are affected. Between the brown and still green parts of the leaves there is a transitional yellowed zone. In the future, the petioles are captured, the leaves dry out. The defeat of root crops begins more often from the top or tip, as places are easier to injure. The spots grow, get wet, acquire an unpleasant odor. This disease is often carried by carrot fly larvae or other pests.
Prevention of carrot diseases

- Selection of healthy root crops for testes. To avoid getting initially infected seeds.
- Correct fertilization. Bust with nitrogen, like neglect of micronutrients, increases the incidence.
- Correct watering. Abundant watering in the heat leads to cracking of root crops, which are further affected by diseases. It is advisable to warm up the water in advance (just let it stand). The addition of mullein solution, microelements, bioactive components improves plant nutrition and increases resistance to diseases.
- Storage processing before storing root crops. Whitewashing, treatment with sulfur bombs or formalin, other septic tanks destroys pathogens in the store and prevents infection.
- Sowing. Excessively thickened plants "drain", forming small roots. At the same time, disease resistance decreases.
- Pest control. Some of the diseases they carry. In addition, damaged vegetables are easier to get sick.
- Agrotechnics. Any deviation from optimal growing conditions leads to weakening of plants and, as a result, increased susceptibility to diseases.
- Choosing a place. Growing in unsuitable - too wet, heavy, acidic soil - weakens the plant. Reduce acidity to the required pH 6.5-7 by introducing calcium-containing additives, preferably under the precursor.
- Limiting injury. Root lesions are the gateway to infection.
- Avoid applying nitrogen before harvesting. Reduces storage stability. With the simultaneous application of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, it is not so critical.
- Stick to crop rotation. Eliminates the accumulation of specific causative agents of carrot diseases in the soil.
- Removal of crop residues. The same goal.
- Growing resistant varieties. Saves time and resources, since such varieties under the same growing conditions are less sick.
Treatment of carrot diseases.
Seed dressing. TMTD or other fungicides are used. Destroys pathogens and short-term, 10-minute, heating in water with a temperature of 52 ˚С.
Sprouted seeds must not be heated!
 Treatment of crops with fungicides. At the moment, a bunch of drugs have been invented. And they come up with more. This is due to both the discovery of new active substances and the marketing moves of manufacturers. It is inappropriate and impossible to give all the norms and doses in this article. It is worth using the instructions for the drugs and your common sense. It is clear to process only after the diagnosis has been established, that is, the type of disease. Do not confuse an infectious disease from frost, heat, hyperdosis or lack of fertilizers.
Treatment of crops with fungicides. At the moment, a bunch of drugs have been invented. And they come up with more. This is due to both the discovery of new active substances and the marketing moves of manufacturers. It is inappropriate and impossible to give all the norms and doses in this article. It is worth using the instructions for the drugs and your common sense. It is clear to process only after the diagnosis has been established, that is, the type of disease. Do not confuse an infectious disease from frost, heat, hyperdosis or lack of fertilizers.
Carrots are mainly affected by fungal diseases. The fact is that the skin of the root vegetables is thin, so they are stored at high humidity to avoid drying out. But it is the high humidity that favors the development of fungal diseases of carrots ...
It is advisable to pay more attention to prevention, and not to abundant spraying of plants after the development of the disease. Easier and more efficient. And you don't have to worry about the residues of poisons in the products.
The lower temperature helps in storage, slows down the development of diseases and loss of goods during storage. It makes sense to reduce the temperature in the storage facility as much as possible, but not below 0 ˚С!