It is important to know tomato diseases in person in order to provide the plant with assistance in a timely manner.
 Diseases of tomato are divided by experts into two large groups - infectious diseases (occurs by the penetration of the pathogen into the body) and non-infectious (caused by abiotic factors).
Diseases of tomato are divided by experts into two large groups - infectious diseases (occurs by the penetration of the pathogen into the body) and non-infectious (caused by abiotic factors).
The causative agents of diseases can be:
- bacteria;
- viruses;
- mushrooms.
Consider how to deal with diseases of each tomato group.
Read also the article: cucumber disease with leaf photo!
Diseases of tomato caused by bacteria
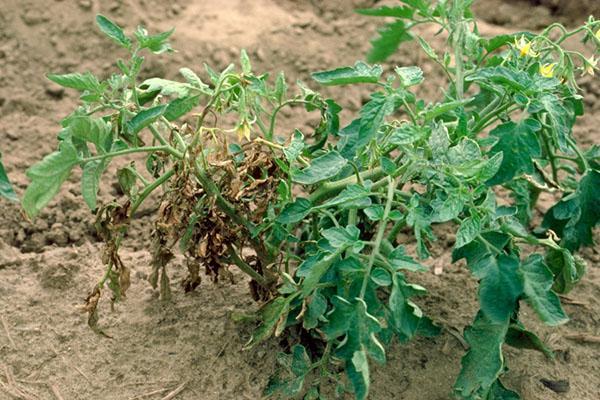

Bacterial mottling
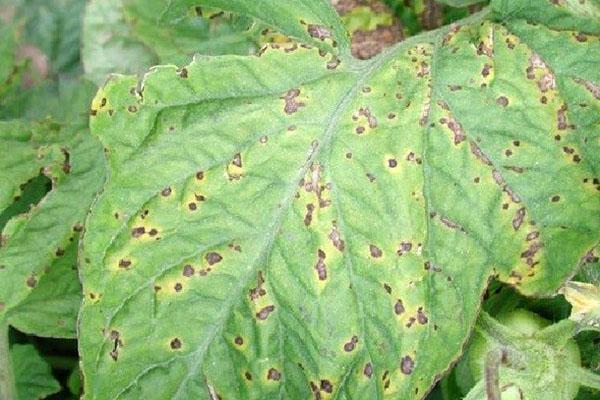 It is not common. The main symptom is leaf damage. First, they are covered with small oily brown spots measuring 2-3 mm, then they roll up and die off. Fruits and stems are infested less frequently.
It is not common. The main symptom is leaf damage. First, they are covered with small oily brown spots measuring 2-3 mm, then they roll up and die off. Fruits and stems are infested less frequently.
Causative agent: Pseudomonas syringae.
Infection occurs from accompanying weeds, at low temperature and high humidity, bacteria multiply.
Prevention: Disinfection of soil and seeds before planting, climate control in the greenhouse.
Treatment: if the infection has already occurred, then the plant is treated with Fitolavin-300 or preparations containing copper (1 glass of copper sulfate per bucket of water). The affected leaves are removed. Reduces air humidity.
Bacterial cancer
 It affects the whole plant: roots, leaves, fruits, seeds. The development of the disease begins with the leaves. With the naked eye, you can see brown growths in the petioles - colonies of bacteria. The stalk is affected from the inside, becomes empty, yellow. White spots appear on the outside of the fruit. The seeds are deformed, do not develop and do not sprout when planted.
It affects the whole plant: roots, leaves, fruits, seeds. The development of the disease begins with the leaves. With the naked eye, you can see brown growths in the petioles - colonies of bacteria. The stalk is affected from the inside, becomes empty, yellow. White spots appear on the outside of the fruit. The seeds are deformed, do not develop and do not sprout when planted.  The plant becomes infectious to others, the infection can be both on the plant itself and in soil, in the seeds. The fruits are unsuitable for food.
The plant becomes infectious to others, the infection can be both on the plant itself and in soil, in the seeds. The fruits are unsuitable for food.
Causative agent: Clavibacter michiganensis.
Prevention: before planting, soak the seeds in TMTD, spray the culture with fungicides.
Treatment: Diseased plants are removed. The protection of healthy bushes is carried out with copper-containing preparations: Bordeaux mixture, Copper sulfate, Copper oxychloride.
Plants are processed in dry weather, observing circadian rhythms: 10.00 - 12.00 and 16.00 - 18.00
Bacterial wilting
 The disease develops rapidly: in a few days, the plant withers before our eyes. Despite the fact that there is enough liquid in the soil, it does not enter the leaves. The stems turn brown on the inside and are empty. Treatment of tomatoes from bacterial wilting is not performed, the plant will have to be destroyed, and the main thing that needs to be done is to protect the rest of the bushes from infection.
The disease develops rapidly: in a few days, the plant withers before our eyes. Despite the fact that there is enough liquid in the soil, it does not enter the leaves. The stems turn brown on the inside and are empty. Treatment of tomatoes from bacterial wilting is not performed, the plant will have to be destroyed, and the main thing that needs to be done is to protect the rest of the bushes from infection.
Causative agent: Pseudomonas solanacearum.
The bacteria live in the soil and infect the roots of plants, blocking blood vessels. You can see how bacterial mucus is released from the affected parts.
Prevention: seed dressing before planting, soil sterilization, harvesting of last year's plant residues.
Treatment: the affected plants are removed, a set of quarantine measures is carried out with a solution of Fitolavin-300 (at least 200 ml for each plant + spraying)
Root cancer
 It is rare, affects the roots. The pathogen is transmitted from other plants through the soil.It can enter the plant through fresh cuts on the roots, wounds. The incubation period is 10-12 days, then growths appear on the roots, inside which there are colonies of bacteria.
It is rare, affects the roots. The pathogen is transmitted from other plants through the soil.It can enter the plant through fresh cuts on the roots, wounds. The incubation period is 10-12 days, then growths appear on the roots, inside which there are colonies of bacteria.
Causative agent: Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
In addition to tomatoes, it affects more than 60 plant species. It can live in soil for several years.
Prevention: sterilizing the soil when planting seeds, processing seedlings in the Fitosporin-M solution (for 1 liter of water - 2-3.2 g), preserving the integrity of the root, avoiding injury during transplantation.
Treatment: the affected plant is removed, the soil of neighboring bushes is treated with solutions of preparations of kartotsid or copper oxychloride.
Wet fruit rot
 The pathogens are spread by insects and other diseased plants. Favorable factors for development are high humidity and temperatures above 28 degrees. For the most part, crops growing in open field are susceptible to the disease. Those varieties of tomatoes that have a generative growth gene for the disease are resistant.
The pathogens are spread by insects and other diseased plants. Favorable factors for development are high humidity and temperatures above 28 degrees. For the most part, crops growing in open field are susceptible to the disease. Those varieties of tomatoes that have a generative growth gene for the disease are resistant.
The disease affects the fruits, they become soft, darken and rot.
Causative agent: Erwinia carotovora.
Prevention: destruction of insect vectors, disinfection of the soil before planting
Treatment: the diseased plant is removed, the neighboring bushes are treated with Fitolavin-300.
Stem necrosis
 The pathogen enters the plant through seeds, soil and other plants. The stems are affected: first, brown spots appear on them, then they increase to the size of warts, the stem bursts, leaves and fruits die.
The pathogen enters the plant through seeds, soil and other plants. The stems are affected: first, brown spots appear on them, then they increase to the size of warts, the stem bursts, leaves and fruits die.
Causative agent: Pseudomonas corrugata.
Prevention: steaming or calcining the soil before planting, because the pathogen dies at temperatures above 41 degrees.
Treatment: the infected culture is destroyed, the soil is treated with a 0.2% solution of Fitolavin-300.
Black bacterial spot of tomato
 Bacteria can destroy up to 50% of the crop, affecting all parts of the plant except the roots. Spots appear on tomatoes, which grow in size and darken over time. The bacteria are very resistant to temperature differences, they can develop both in cold and hot weather, and remain on seeds for a year and a half. They die only at temperatures above 56 degrees.
Bacteria can destroy up to 50% of the crop, affecting all parts of the plant except the roots. Spots appear on tomatoes, which grow in size and darken over time. The bacteria are very resistant to temperature differences, they can develop both in cold and hot weather, and remain on seeds for a year and a half. They die only at temperatures above 56 degrees.
Causative agent: Xanthomonas vesicatoria.
Prevention: seed treatment before planting with Phytolavin-300 or trisodium phosphate, preventive treatment of seedlings 1 time in 2 weeks 1% Bordeaux mixture and Cartocide.
Treatment: the plant is isolated, the affected areas are removed, neighboring bushes and soil are treated with fungicides.
Diseases initiated by viruses
 The causative agents are viruses, hundreds of times less bacteria. There are no drugs against viral diseases of tomatoes, so the infected plant must be isolated and destroyed. The carriers are both parts of infected plants and insect pests... Much attention should be paid to prevention, which includes a whole range of measures to combat tomato diseases:
The causative agents are viruses, hundreds of times less bacteria. There are no drugs against viral diseases of tomatoes, so the infected plant must be isolated and destroyed. The carriers are both parts of infected plants and insect pests... Much attention should be paid to prevention, which includes a whole range of measures to combat tomato diseases:
- soil treatment before planting: disinfection, calcination;
- preparation of seed material, preliminary disinfection;
- isolation of diseased plants;
- adherence to planting rules: distance between bushes, water and light conditions;
- compatibility with other crops, do not plant tomatoes next to plants that are potential carriers of viruses, remove weeds;
- insect pest control.
Aspermia
 Another name is seedlessness. The virus infects the generative parts of the plant. Flowers grow together, deform, seeds do not ripen in fruits. In the photo of tomatoes suffering from aspermia, it can be seen that the leaves of the plant become small, the stem is weak, the peduncles do not develop.
Another name is seedlessness. The virus infects the generative parts of the plant. Flowers grow together, deform, seeds do not ripen in fruits. In the photo of tomatoes suffering from aspermia, it can be seen that the leaves of the plant become small, the stem is weak, the peduncles do not develop.
Causative agent: Tomato aspermy cucumovirus.
Aspermia virus spreads to tomatoes from insects or other plants (such as chrysanthemums)
Preventive measures include:
- isolation and destruction of diseased plants in greenhouses;
- fight against aphids;
- weed control;
- to divide geographically tomatoes and chrysanthemums.
Bronze
 A sign of leaf bronzing virus infection is the appearance of a characteristic pattern on fruits and leaves in the form of brownish rings. The main vectors are thrips. The virus dies at temperatures over 45 degrees.
A sign of leaf bronzing virus infection is the appearance of a characteristic pattern on fruits and leaves in the form of brownish rings. The main vectors are thrips. The virus dies at temperatures over 45 degrees.
Causative agent: Tomato spotted wilt virus.
Prevention: calcination of the soil before planting seeds, destruction of thrips.
Yellow curl
 The curl virus in tomatoes affects the leaves, which become small, deformed, and unevenly colored. The bush does not grow in height, the fruits are not tied.
The curl virus in tomatoes affects the leaves, which become small, deformed, and unevenly colored. The bush does not grow in height, the fruits are not tied.
Causative agent: Tomato yellow leaf curl virus.
Prevention: Whiteflies are the most common carriers of the virus. Therefore, preventive measures are aimed at preventing the reproduction of these insects.
Top toughness
 The manifestation of the disease is first noticed on the leaves. White dots appear on them, which then darken. The leaf blades become rough, the veins turn blue, the leaf itself curls at an acute angle. The bush takes on the shape of a spindle.
The manifestation of the disease is first noticed on the leaves. White dots appear on them, which then darken. The leaf blades become rough, the veins turn blue, the leaf itself curls at an acute angle. The bush takes on the shape of a spindle.
Causative agent: Tomato bunchy top viroid.
Prevention: Aphids, infected seeds become the carrier of the virus. The virus is deactivated at a temperature of 75 degrees. Preventive measures include tillage before planting and destruction of aphid colonies.
Mosaic
 Infection occurs from diseased seeds. Most often found in plants grown outdoors. The leaves are covered with light and dark spots, like a mosaic, on the fruits there are yellow spots.
Infection occurs from diseased seeds. Most often found in plants grown outdoors. The leaves are covered with light and dark spots, like a mosaic, on the fruits there are yellow spots.
Causative agent: Tomato mosaic tobamovirus.
Prevention:
- Seed treatment before planting.
- The diseased plant is removed.
- Dead bushes are burned.
- From folk remedies, it is proposed to process young bushes 3 times a month with milk and urea.
Stolbur (phytoplasmosis)
 Infection manifests itself on leaves, stems, flowers and fruits. Leaves change color, first turn pink, then darken, become rough and brittle. The edges are wrapped and the sheet becomes like a boat. Flowers grow together, lengthen, petals remain small. Usually the fruits do not form from them, or small tomatoes appear, with an uneven color, white and hard on the inside. You cannot eat them.
Infection manifests itself on leaves, stems, flowers and fruits. Leaves change color, first turn pink, then darken, become rough and brittle. The edges are wrapped and the sheet becomes like a boat. Flowers grow together, lengthen, petals remain small. Usually the fruits do not form from them, or small tomatoes appear, with an uneven color, white and hard on the inside. You cannot eat them.
Most often, the virus infects southern cultures, its main carriers are cicadas.
Causative agent: Lycopersicum virus 5 Smith.
Prevention: disinfection of planting material and soil, isolation of tomatoes from other vegetable crops, control of insect vectors.
Fungal diseases of tomatoes
 The fungus can infect any part of the plant. This is the most common group of diseases.
The fungus can infect any part of the plant. This is the most common group of diseases.
Fungi that cause fruit rot are called rot. It can be of different types: brown rot of tomatoes, black, white, gray, root, apical. The nature of the lesions and preventive measures are common. Consider several types of rot.
White rot
 The fungus enters the plant through the soil. The fruits are covered with weeping white putrefactive spots.
The fungus enters the plant through the soil. The fruits are covered with weeping white putrefactive spots.
Most often, damaged areas are affected - in tears of the skin of the fetus with excessive growth, mechanical damage, as well as in violation of transportation and storage conditions.
Causative agent: fungus of the genus Sclerotinia.
Prevention: disinfection of the soil during planting, compliance with the rules of transportation and storage.
Treatment: Treatment of plants with a solution of copper sulfate, urea and zinc, diluted in water.
Gray rot
 It can destroy 50% of the crop. The mycelium of the fungus penetrates the stem and fruits, tissue necrosis develops, they soften and become covered with a gray bloom. The spores of the fungi are very viable and remain in the soil for several years. They can also be spread from other crops (for example, cucumbers). The infection is spread by air and water.
It can destroy 50% of the crop. The mycelium of the fungus penetrates the stem and fruits, tissue necrosis develops, they soften and become covered with a gray bloom. The spores of the fungi are very viable and remain in the soil for several years. They can also be spread from other crops (for example, cucumbers). The infection is spread by air and water.
Causative agent: fungus of the genus Botrytis cinerea.
Prevention:
- decrease in air humidity in the greenhouse;
- removal of infected plants;
- avoid small wounds and cuts through which infection can occur;
- periodic disinfection of greenhouses.
Treatment: chemicals (Bayleton, Euparen), treatment with sodium humate. An effective remedy is coating lesions with fungicidal paste mixed with CMC glue. This procedure must be repeated once every 2 weeks so that new spots do not appear.
Root rot of tomatoes
 Another name is black leg. It is caused by the appearance of the affected area: the upper part of the root at the root collar turns black and rots. The whole plant then dies. The fungus spreads in moist soil, remains on plant debris and seeds. Primary infection occurs from old soil and peat. Excessive moisture aggravates the disease.
Another name is black leg. It is caused by the appearance of the affected area: the upper part of the root at the root collar turns black and rots. The whole plant then dies. The fungus spreads in moist soil, remains on plant debris and seeds. Primary infection occurs from old soil and peat. Excessive moisture aggravates the disease.
Causative agents: fungi of the genus Rhizoctonia solani.
Prevention: observe the irrigation regime, disinfect seeds and soil before planting, for example, with Pseudobacterin-2 at the rate of 1: 100 l of water, sulfur-containing preparations are also effective
Treatment: remove the affected plant from the root, treat the soil with 0.25% suspension of Ridomil Gold, do not plant tomatoes in this place for 1 year.
The next group of fungi infect the leaves with different spots. Hence their name - spotting. Distinguish between black, gray, white, brown, yellow spot on tomato leaves.
Septoria
 Another name is white spot. The fungus infects the leaves, they become covered with light spots, deformed and dry out. The most favorable conditions for fungus are temperatures from 15 to 27 degrees and humidity from 77%. The fungus remains on the remains of the plant.
Another name is white spot. The fungus infects the leaves, they become covered with light spots, deformed and dry out. The most favorable conditions for fungus are temperatures from 15 to 27 degrees and humidity from 77%. The fungus remains on the remains of the plant.
Causative agent: Septoria lycopersici fungus.
Prevention: removing plant debris, keeping the distance when planting, isolating tomatoes from other nightshades.
Treatment: spraying with fungicides.
Cladosporium
 The second name is brown spot. It affects the leaves, on which orange-brown spots appear, which eventually darken and become covered with bloom. Like all mushrooms, the causative agent of tomato disease develops at high humidity and temperature. Disputes persist for up to 10 years. Breeders are constantly improving tomato varieties, breeding cladosporium-resistant species.
The second name is brown spot. It affects the leaves, on which orange-brown spots appear, which eventually darken and become covered with bloom. Like all mushrooms, the causative agent of tomato disease develops at high humidity and temperature. Disputes persist for up to 10 years. Breeders are constantly improving tomato varieties, breeding cladosporium-resistant species.
Causative agents: fungi of the genus Passalora fulva and Cladosporium fulvum.
Prevention: the use of varieties that are immune to the disease.
Treatment: spraying with drugs: HOM, Abiga-Peak, Poliram.
Macrosporiasis
 Another name is the gray spot of tomato leaves. The etiology of the disease is still the same. Gray-brown spots are formed on the affected leaves. They increase in size, join together, affecting the leaf tissue. The plant withers.
Another name is the gray spot of tomato leaves. The etiology of the disease is still the same. Gray-brown spots are formed on the affected leaves. They increase in size, join together, affecting the leaf tissue. The plant withers.
Causative agents: mushrooms of the genus Stemphylium solani.
Prevention: reorganization of soil and seeds before planting, observance of the light regime.
Treatment: spraying with fungicides.
Alternaria
 The fungus affects the leaves, stems and fruits of tomatoes. At first, the disease progresses on the leaves, they become covered with large spots of dark brown color and gradually dry out. The stem also darkens and dies off. On fruits, spots are formed at the stalk, with sufficient moisture, fungal spores develop. The top of the tomato becomes dark, depressed, with a velvet bloom. The fungus grows especially quickly at temperatures of 25-30 degrees and high humidity.
The fungus affects the leaves, stems and fruits of tomatoes. At first, the disease progresses on the leaves, they become covered with large spots of dark brown color and gradually dry out. The stem also darkens and dies off. On fruits, spots are formed at the stalk, with sufficient moisture, fungal spores develop. The top of the tomato becomes dark, depressed, with a velvet bloom. The fungus grows especially quickly at temperatures of 25-30 degrees and high humidity.
Causative agent: mold Alternaria solani Sorauer.
Prevention: treatment of seeds and soil with antifungal agents ("Trichodermin", "Fitosporin", etc.), choose varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to the disease.
Treatment: treatment with copper-containing drugs (Ridomil Gold, Skor) during the vegetative period, if fruits have appeared - biological products.
Tomatoes cannot be planted in a place where potatoes, eggplants, cabbage, peppers used to grow.
Anthracnose
 Adult plants get sick with anthracnose of tomatoes. The fungus can infect leaves and fruits. In the first case, the leaves wither, the stem is bare, the roots are deformed, become weak and thin, the plant easily breaks out. On the affected parts, you can see small black seals consisting of the mycelium of the fungus.
Adult plants get sick with anthracnose of tomatoes. The fungus can infect leaves and fruits. In the first case, the leaves wither, the stem is bare, the roots are deformed, become weak and thin, the plant easily breaks out. On the affected parts, you can see small black seals consisting of the mycelium of the fungus.
If the fungus has infected the fruits, then they are covered with depressed flat spots.
Causative agent: fungi of the genus Colletotrichum.
Prevention: seed treatment with Agat-25, during the growing season - Quadris or Strobi, or on the basis of a hay stick.
Treatment: During the development of the disease, gardeners recommend spraying the bushes with Poliram with a consumption rate of 2.53 kg / ha.
Verticillosis
 Fungal disease that affects old tomato leaves. Chlorophyll production is impaired, so the leaves fade and die off. The mycelium of the fungus is resistant to temperature extremes and persists for a long time in the soil and on plant residues. Later, roots and stems become infected. The disease spreads from bottom to top up to 1 m in height. There are no drugs that completely defeat fungal spores. When choosing tomato varieties, one should pay attention to the resistance to verticillium.
Fungal disease that affects old tomato leaves. Chlorophyll production is impaired, so the leaves fade and die off. The mycelium of the fungus is resistant to temperature extremes and persists for a long time in the soil and on plant residues. Later, roots and stems become infected. The disease spreads from bottom to top up to 1 m in height. There are no drugs that completely defeat fungal spores. When choosing tomato varieties, one should pay attention to the resistance to verticillium.
Causative agent: fungi of the genus Verticillium.
Prevention: the use of varieties that are immune to the disease.
Treatment: the diseased plant is removed, fresh soil is laid out in its place, the soil is rehabilitated using crops such as rye, peas, mustard. They promote the development of microorganisms that destroy harmful fungi.
Powdery mildew
 Capable of striking huge areas. Microscopic spores of the fungus appear as white bloom on tomato leaves. The affected plant is deformed. Parts of the leaf become discolored, the plant weakens and dies. Most often it develops indoors.
Capable of striking huge areas. Microscopic spores of the fungus appear as white bloom on tomato leaves. The affected plant is deformed. Parts of the leaf become discolored, the plant weakens and dies. Most often it develops indoors.
Causative agent: marsupial mushrooms of the genus Oidium erysiphoides Fr.
Prevention: use of varieties that are immune to the disease, taking measures to disinfect greenhouses.
Treatment: spraying with fungicides, sodium humate 0.1 and 0.01% completely destroys the fungus, Topaz, Quadris, Strobi preparations are also effective.
Ascochitosis
 The second name is stem cancer, due to the fact that the fungus first affects the stems of plants, and then the disease passes to the leaves and fruits. The affected areas darken, depressed weeping spots appear on them. Cold and humid weather contributes to the development of the fungus. The spores of the fungus persist for a long time in the soil, on plant debris and seeds. Most often it affects greenhouse plants, rarely found outdoors.
The second name is stem cancer, due to the fact that the fungus first affects the stems of plants, and then the disease passes to the leaves and fruits. The affected areas darken, depressed weeping spots appear on them. Cold and humid weather contributes to the development of the fungus. The spores of the fungus persist for a long time in the soil, on plant debris and seeds. Most often it affects greenhouse plants, rarely found outdoors.
Causative agent: fungi of the genus Ascochyta lycopersici.
Prevention: soil and seed treatment before planting, temperature rise with reduced humidity, greenhouse ventilation.
Treatment: treatment of spots with a special chalk paste, spraying with growth regulators (Agat-25, Immunocytophyte)
Fusarium wilting
 A fairly common disease among nightshades. There are varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to the fungus of Fusarium, you should pay attention to this when planting. If there is no such mark, then it is worth taking preventive measures to avoid infection.
A fairly common disease among nightshades. There are varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to the fungus of Fusarium, you should pay attention to this when planting. If there is no such mark, then it is worth taking preventive measures to avoid infection.
The disease manifests itself on the leaves and develops from the bottom up. First, chlorosis spots appear, then the leaf is deformed and the shoots wither. If you put a sprig of an infected plant in a glass of water, you can see white mycelial filaments of mushrooms in 1-2 days.
The fungus causes especially great harm to greenhouse crops, affecting the vascular system of plants. Infection occurs from plant debris.
Causative agent: fungi of the genus Fusarium oxysporum.
Prevention: Tilling the soil before planting with Pseudobacterin-2, benzenemidazole, observing crop rotation, conducting microbiological reclamation.
Treatment: Trichodermin, Benazol, Planriz are effective drugs to combat the fungus.
Late blight
 A common disease of tomatoes in the open field. The mycelium of the fungus infects the root system and stem through the soil. The leaves are covered with red spots, on the reverse side you can see a bloom of light gray. Hard brown spots form on the fruits, they rot and fall off. Infection can occur from other nightshades (eg potatoes).
A common disease of tomatoes in the open field. The mycelium of the fungus infects the root system and stem through the soil. The leaves are covered with red spots, on the reverse side you can see a bloom of light gray. Hard brown spots form on the fruits, they rot and fall off. Infection can occur from other nightshades (eg potatoes).
Causative agent: fungi of the genus Phytophthora infestans.
Prevention: sterilization of the soil before planting, treatment with Pseudobacterin -2, during the growing season - with sodium humate.
Treatment: removal of infected parts of the plant, spraying the plants with 0.5-1% Baktofit solution with an interval of 8 days or with Agat-25.
Diseases of tomatoes caused by abiotic factors
These include genetic disorders, adverse weather conditions, and improper care.
Top rot of fruit
 It develops in large fruits due to unfavorable soil or genetic disorders with a lack of calcium ions. The fruits are covered with brown spots on the top, which sometimes take up a third of the tomato.
It develops in large fruits due to unfavorable soil or genetic disorders with a lack of calcium ions. The fruits are covered with brown spots on the top, which sometimes take up a third of the tomato.
Prevention: the use of calcium-containing fertilizers, adherence to the irrigation regime.
Hollow fruit
 With the disease, seeds are not formed. Occurs with disturbances in pollination processes and a lack of nutrients (especially potassium)
With the disease, seeds are not formed. Occurs with disturbances in pollination processes and a lack of nutrients (especially potassium)
Prevention: adherence to recommendations for growing tomato crops, irrigation regime, soil selection, dressing.
Fruit cracking
 Cracks on tomatoes appear when there is an excess of moisture in the soil. This happens after heavy rain or watering, especially in crops with large fruits and thin skin. This phenomenon is not dangerous for the health of the whole plant. The fruits remain edible, but it is advisable to remove them from the bush as soon as cracking is noticed, since rot spores can settle on the wound.
Cracks on tomatoes appear when there is an excess of moisture in the soil. This happens after heavy rain or watering, especially in crops with large fruits and thin skin. This phenomenon is not dangerous for the health of the whole plant. The fruits remain edible, but it is advisable to remove them from the bush as soon as cracking is noticed, since rot spores can settle on the wound.
Large varieties usually burst radially, while small ones, for example, cherry - round. Prevention consists in observing the watering regime and the timely collection of large fruits.
Scarring (ugly tomato)
 Found in large-fruited varieties. This phenomenon is a consequence of the splicing of flowers. The reason is the predominance of nitrogen in the soil and the lack of phosphorus. The bush grows, the flowers do not separate. They are called "terry". The result is a giant irregularly shaped fetus with scars - "fasteners". Prevention - remove already formed double flowers, monitor the mineral composition of the soil.
Found in large-fruited varieties. This phenomenon is a consequence of the splicing of flowers. The reason is the predominance of nitrogen in the soil and the lack of phosphorus. The bush grows, the flowers do not separate. They are called "terry". The result is a giant irregularly shaped fetus with scars - "fasteners". Prevention - remove already formed double flowers, monitor the mineral composition of the soil.
Yellow tomato disorder
 With a lack of organic matter in the soil, high acidity and low phosphorus content, the disease of uneven ripening of fruits "yellow disorder" can develop. These tomatoes never fully ripen and remain half yellow. On the inside, they are light, hard and tasteless. The way out is to establish mineral metabolism in plant nutrition.
With a lack of organic matter in the soil, high acidity and low phosphorus content, the disease of uneven ripening of fruits "yellow disorder" can develop. These tomatoes never fully ripen and remain half yellow. On the inside, they are light, hard and tasteless. The way out is to establish mineral metabolism in plant nutrition.
Sunburn
 Tomatoes do not like direct sunlight and heat. Leaves and fruits can get sunburn. The area in these places is discolored. Rot spores can penetrate the fruit wounds, so it is better to remove it from the bush. For prevention, choose places for tomatoes that are shady, with well-drained soil, or install light filters.
Tomatoes do not like direct sunlight and heat. Leaves and fruits can get sunburn. The area in these places is discolored. Rot spores can penetrate the fruit wounds, so it is better to remove it from the bush. For prevention, choose places for tomatoes that are shady, with well-drained soil, or install light filters.
Oedema
 It appears as small bumps on tomato leaves. This phenomenon occurs due to improper watering, violation of turgor and water-salt metabolism. It is necessary to rearrange the plant to a more spacious place, ventilate and treat with copper-containing preparations.
It appears as small bumps on tomato leaves. This phenomenon occurs due to improper watering, violation of turgor and water-salt metabolism. It is necessary to rearrange the plant to a more spacious place, ventilate and treat with copper-containing preparations.
Blue foliage and stem
 Sometimes, after transplanting seedlings, gardeners observe a change in the color of the plant: the stem of the tomato turns blue, and the leaves acquire a shade of purple. Most often this happens due to a sharp change in temperature. If no other signs (wilting, the appearance of spots, etc.) are observed, then there is nothing to worry about - the color will recover as soon as the temperature rises above 15 degrees.
Sometimes, after transplanting seedlings, gardeners observe a change in the color of the plant: the stem of the tomato turns blue, and the leaves acquire a shade of purple. Most often this happens due to a sharp change in temperature. If no other signs (wilting, the appearance of spots, etc.) are observed, then there is nothing to worry about - the color will recover as soon as the temperature rises above 15 degrees.
For the plant to be stress-resistant to climatic changes, it must be hardened!
External changes may indicate a lack of trace elements for the plant. The table below shows the signs by which you can analyze the sufficiency of inorganic elements in the diet of tomatoes.
Breeders and agronomists are offering all new methods of combating tomato diseases. In the arsenal of the gardener there are biological products, chemicals, new varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to fungal diseases. A complex of agrotechnical measures, compliance with planting rules, timely prevention will help preserve the harvest.