Diseases of ducks: causes, varieties, methods of treatment
 Ducks have good immunity. However, even the toughest birds can overtake diseases of ducks. Diseases in adult birds and young animals are divided:
Ducks have good immunity. However, even the toughest birds can overtake diseases of ducks. Diseases in adult birds and young animals are divided:
- for infectious diseases caused by protozoa, viruses and bacteria, helminths, ticks and other parasites;
- on non-infectious, not spreading among the rest of the livestock and people.
Both those and other ailments cause serious damage to the economy and without urgent and, most importantly, effective measures, they can destroy most of the strong promising livestock.
Common causes of disease in ducks

To prevent the death of young animals, and then already grown ducks, first of all, you need to monitor:
- the conditions for keeping poultry, temperature conditions, cleanliness of premises and equipment;
- compliance with the norms of planting ducks per unit area;
- for the quality of the given drink and feed, its balance and freshness.
If you do not adhere to these rules, the bird weakens, becomes open to attack by dangerous infections and parasites.
At the first sign of illness, suspicious ducks and ducklings should be isolated.
Depending on the symptoms of the disease, ducks are treated for parasites, treated with antibiotics or other specialized drugs, prescribed a course of vitamins, or simply brought the growing conditions to the recommended sanitary and hygienic standards.
Avitaminosis and their treatment in ducks
Improper feeding combined with poor living conditions of the bird leads to a weakening of the immune system, slowing or stunting of growth. In adult females, egg production drops, the bird takes on a disheveled, unkempt appearance. All these and other signs indicate the possibility of disease in ducks. Most often, non-communicable diseases are associated with lack of vitamins, minerals and a general weakening of the livestock.
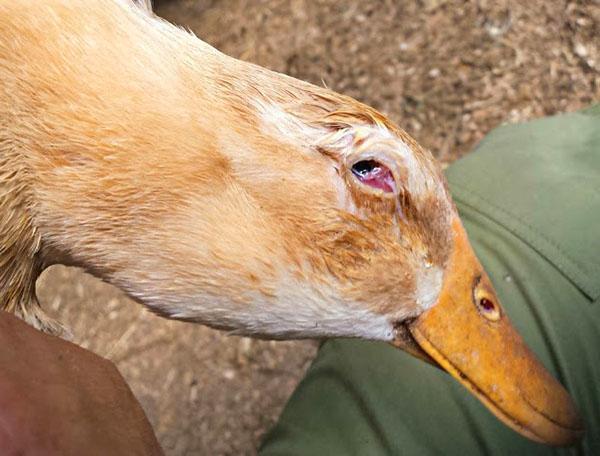 Avitaminosis caused by improper maintenance and nutrition is not considered by many novice poultry farmers to be serious ailments. But in vain! Symptoms of a vitamin A deficiency, for example, in an advanced form, look very threatening:
Avitaminosis caused by improper maintenance and nutrition is not considered by many novice poultry farmers to be serious ailments. But in vain! Symptoms of a vitamin A deficiency, for example, in an advanced form, look very threatening:
- The ducks lose their appetite.
- They suffer from inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and eyes.
- Not for the better, the appearance of plumage changes, which becomes disheveled, dirty.
- Legs and beak fade.
- Such a bird begins to lag behind in growth, and this lag only increases with time.
- The bird's gait changes, becomes uneven. Some ducks fall to their feet, refuse to drink and feed.
 Regular inclusion of foods rich in carotene and vitamin A in the diet is a good prevention and treatment of duck disease. These include:
Regular inclusion of foods rich in carotene and vitamin A in the diet is a good prevention and treatment of duck disease. These include:
- root crops and carrot tops;
- clover and alfalfa greens;
- needles;
- silage and grass meal, hay in winter;
- steamed nettles.
In addition, you should not deny the bird aquatic vegetation.
With pronounced vitamin deficiency and young animals, they must be given fish oil.
 Similar measures with supplementing the diet with mineral feed, yeast and allowing the birds to walk are necessary if ducks suffer from vitamin D deficiency.Symptoms of this disease of ducks, threatening the feathered development of rickets, are:
Similar measures with supplementing the diet with mineral feed, yeast and allowing the birds to walk are necessary if ducks suffer from vitamin D deficiency.Symptoms of this disease of ducks, threatening the feathered development of rickets, are:
- in poor growth and weight gain;
- weakness of the limbs, as a result of which such ducks fall;
- in softening of the beak and curvature of the paws.
Adults do not lay well, and emerging eggs are shellless or have poorly formed, pliable shells.
 The lack of B vitamins in the feed leads to nervousness of the bird, cramps and weakness of the limbs. With a severe illness, ducks can be paralyzed. Treatment and prevention in this case consists in the active inclusion of yeast, sprouted grains, bran, herbs and other foods rich in vitamins and microelements in the menu.
The lack of B vitamins in the feed leads to nervousness of the bird, cramps and weakness of the limbs. With a severe illness, ducks can be paralyzed. Treatment and prevention in this case consists in the active inclusion of yeast, sprouted grains, bran, herbs and other foods rich in vitamins and microelements in the menu.
Non-contagious diseases of ducks
If ducks are deficient in several components of the vitamin set at once, poultry farmers are faced with the manifestation of cloacite.
 This disease of ducks, associated with inflammation of the mucous membranes in the area of the cloaca, is often triggered by a lack of vitamins A and E. Young ducks are most susceptible to the disease. To exclude the development of the disease, more greens are included in the feed, chopped carrot roots, pumpkinand, in winter, grass flour and multicomponent vitamin silage.
This disease of ducks, associated with inflammation of the mucous membranes in the area of the cloaca, is often triggered by a lack of vitamins A and E. Young ducks are most susceptible to the disease. To exclude the development of the disease, more greens are included in the feed, chopped carrot roots, pumpkinand, in winter, grass flour and multicomponent vitamin silage.
In the poultry house and on the walk, a feeder with a crushed shell and chalk must be installed, bone meal is introduced into the menu, and the bird is provided with water and under the open sky.
If the mucous membrane is damaged, there is a possibility of suppuration or inflammatory processes are already actively going on:
- the cloaca of such a bird is washed with clean water;
- cleanse of pus;
- treated with an alcoholic solution of iodine.
After that, as part of the treatment of ducks, wounds can be treated with local drying agents, as well as antibiotic ointments.
Together with cloacite, young ducks may experience another disease - prolapse of the oviduct. This happens when large, often double-yolk or irregularly shaped eggs form. It is possible that the cause of the unpleasant symptoms and illness of ducks lies in improper diet and the resulting diarrhea and constipation. The oviduct is washed with a pink solution of potassium permanganate and adjusted. To eliminate clogging of the goiter and esophagus, the introduction of vegetable oils is used.
 When poultry is kept in dirty, damp rooms, ducks suffer from overcrowding, lack of protein and mineral salts, poultry breeders observe symptoms of pecking. Showing signs of a kind of cannibalism, ducks pluck out feathers and can peck to death on their weaker relatives. Ducks can lose feathers on their own, and this does not happen during molting, but because of dirty litter, crowding.
When poultry is kept in dirty, damp rooms, ducks suffer from overcrowding, lack of protein and mineral salts, poultry breeders observe symptoms of pecking. Showing signs of a kind of cannibalism, ducks pluck out feathers and can peck to death on their weaker relatives. Ducks can lose feathers on their own, and this does not happen during molting, but because of dirty litter, crowding.
And in such a situation, putting things in order in the poultry house, ensuring walking and restoring a balanced diet will help. Birds with signs of cannibalism are removed, and the most aggressive are sent to slaughter.
Duck infectious diseases, symptoms and treatment
Infectious diseases of ducks are dangerous both for the birds themselves and for other inhabitants of the poultry yard, and sometimes for humans.
 The disease, accompanied by tearing, sticking eyes, indigestion, lack of appetite and lethargy, is most often paratyphoid. Duck disease with the symptoms described above kills most of the herd and affects the youngest part of the herd.
The disease, accompanied by tearing, sticking eyes, indigestion, lack of appetite and lethargy, is most often paratyphoid. Duck disease with the symptoms described above kills most of the herd and affects the youngest part of the herd.
The source of infection is the ducklings infected in the egg. Even after successful treatment of the disease, ducks remain carriers of the causative agent of the disease, which is dangerous for the people who maintain the poultry house.
Pasteurellosis or cholera of poultry gets into poultry houses with sick individuals, and with rodents running into the room, with insects and mites parasitizing on ducks. The infection can be transmitted by other domestic animals with which the bird is adjacent to the walk.
 Increasingly, poultry farmers are detecting hepatitis in poultry.This is a viral lesion of the liver of ducks, which most negatively affects health and behavior. The sick bird is very reluctant to move, it is drowsy, apathetic, breathing heavily and eating poorly. At the serious stage, ducks fall, toppling on their side with their heads thrown back and outstretched limbs. Death is almost inevitable.
Increasingly, poultry farmers are detecting hepatitis in poultry.This is a viral lesion of the liver of ducks, which most negatively affects health and behavior. The sick bird is very reluctant to move, it is drowsy, apathetic, breathing heavily and eating poorly. At the serious stage, ducks fall, toppling on their side with their heads thrown back and outstretched limbs. Death is almost inevitable.
With all of these diseases, treatment of ducks can be ineffective and difficult. On the other hand, the preventive measures taken in time ensure that the formidable diseases of ducks can be avoided.
Helminthiasis and other parasitic diseases of ducks
 All waterfowl, including ducks, are susceptible to helminth infestation. Diseases of this type are especially dangerous for birds sharing one body of water with cattle, pigs and other inhabitants of cattle yards.
All waterfowl, including ducks, are susceptible to helminth infestation. Diseases of this type are especially dangerous for birds sharing one body of water with cattle, pigs and other inhabitants of cattle yards.
Symptoms of worm-related disease in ducks include:
- slowdown and arrest in growth and weight gain;
- changing attitudes towards food;
- lethargy;
- depletion regardless of the diet used.
In addition, worms cause a decrease in the productivity of layers, and in some cases, parasites even infect embryos. When signs of illness appear, treatment of ducks is undertaken immediately and in relation to the entire herd.
As a preventive measure:
- birds must be fed green onions, greens of garlic, chopped needles, pumpkin and zucchini pulp;
- regularly disinfect poultry houses, feeders and drinkers, as well as artificial reservoirs on walking grounds;
- periodically change places of walking;
- do not allow contact with other farm animals.
Similarly, poultry is regularly treated against ticks, fleas, and chewing lice. For the independent fight of ducks with skin parasites, the birds are provided with bathing places.
In the protection of ducks from infectious and non-infectious diseases, the main role is played by the observance of hygiene rules, careful attention to the livestock and the supply of high-quality feed to the poultry.
If you follow these simple rules, the poultry farmer will not have to deal with the symptoms of diseases of ducks and their treatment.
I cured my ducks, I didn't have enough vitamins. All healthy and happy chicks, thank you!
How to cure dizziness in ducklings