How is the gable roof rafter system
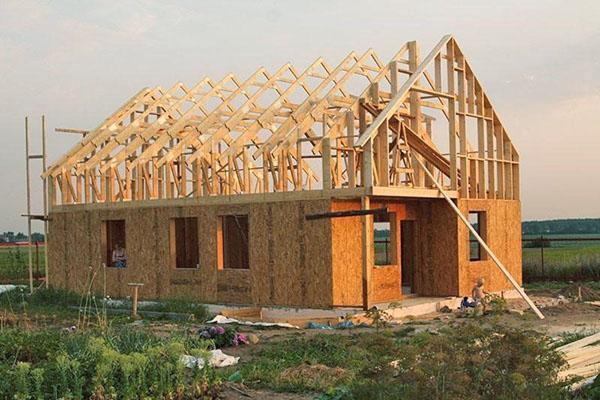 The practicality, reliability and simplicity of the gable roof design make it available for self-erection even for a novice developer. In this publication, the rafter system of a gable roof will be considered in detail: its varieties, structural elements and calculation rules.
The practicality, reliability and simplicity of the gable roof design make it available for self-erection even for a novice developer. In this publication, the rafter system of a gable roof will be considered in detail: its varieties, structural elements and calculation rules.
Gable roof rafter system

The purpose of the rafter system
The gable roof rafter system solves three main tasks:
- Giving the roof slopes the required angle of inclination, which allows them to withstand the maximum snow and wind loads for a given area, makes it possible to unhindered water and snow from the roofing material.
- Uniform distribution of loads on the building frame, created by the weight of the roofing cake, precipitation, wind.
- Creation of the basis for fastening the thermal insulation of the roofing material. The nodes of the rafter system of a gable roof with a roof create a space that protects the building from heat loss and moisture penetration.
A properly designed rafter system must withstand very serious loads, which can exceed 500 kg / m2.
That is why we recommend entrusting all calculations related to the choice of material, section and installation pitch of rafters to professionals who have permission and experience in performing such work.
As noted above, a roof cut with two slopes is an isosceles triangle. The horizontal plane of the triangle rests on the walls of the building. Inclined planes are nothing more than roof slopes. The angle of inclination of the slopes is formed by the angle between the base of the roof and its ridge.
Basic structural elements
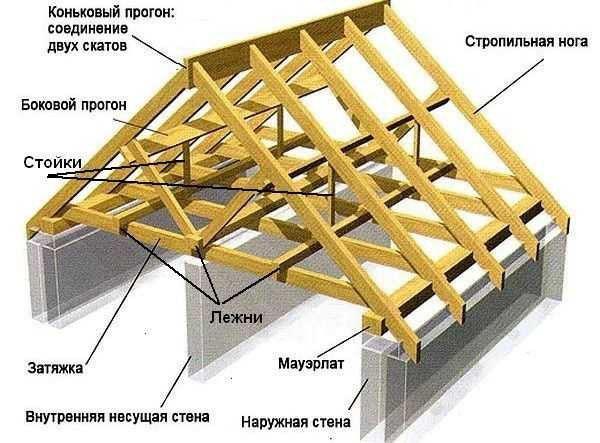
For ease of understanding of this design, we will consider the main elements of the rafter system of a gable roof:
- Rafter legs are the main structural elements of the frame, due to which the necessary inclination of the roof planes is created. The planes formed by the rafter beams are the basis for the installation of the flooring.
- Mauerlat is a supporting structure element that is attached to the upper end of the outer walls of the building. Mauerlat for a gable roof allows you to distribute the mass of the roof structure as evenly as possible.
- Tightens are transverse elements of the frame, connecting paired rafters into a single unit. The main purpose of the puffs is to increase the rigidity of the entire system.
- The beds are located parallel to the Mauerlats and connect the puffs. They use the upper end of the internal load-bearing walls as support. Purpose - distribution of impacts on the rafter system.
- Floor beams are installed between the Mauerlats and the bed. They serve as the basis for fixing the floor in the attic and the ceiling of the building. The beams are installed on the braces.
- The ridge girder connects the upper parts of the rafters.This structural element is used in most rafter system construction schemes.
- Side girder is an additional structural element that supports the rafters and removes some of the load from them.
- Racks (headstock) are the main structural elements of the frame reinforcement system, which take on some of the loads from the runs.
In some schemes, auxiliary structures are used - filly - to ensure the creation of a cornice overhang of the roof with a shortage of the length of the rafter legs.
The roof frame can be represented as three nodes:
- The lathing is the basis for fastening the insulating layer and roofing material. Mounted on rafters. The rafter legs with the lower end rest on the Mauerlat, with the upper end on the rafter system
- The main rafter system, made in the form of a mounted rafter bar.
- A rafter system is a specific set of additional frame elements: purlins and racks. With an increase in the span length, additional structural elements are used - struts. Among the masters, another name for the braces is in use - "rafter legs". Regardless of the name, the main purpose of these elements is to support side girders. One end of the brace rests against the rafter beam, the other against the bed. The rafter braces play an essential role in the roof frame - they prevent deformation of the rafter leg and significantly increase its bearing capacity.
Design features and types of rafter systems for a gable roof
 Rafter legs are the main element of any gable roof frame. Depending on the geometry and size of the roof, all other structural elements of the frame may not be used or partially used during its construction.
Rafter legs are the main element of any gable roof frame. Depending on the geometry and size of the roof, all other structural elements of the frame may not be used or partially used during its construction.
By the method of installing the legs, the scheme of the roof rafter system can be:
- layered type;

- hanging type.

The main condition for the installation of layered rafters is the arrangement of reliable support in the upper and lower parts. The horizontal ridge unit of the rafter roof acts as a support for the upper part. The lower edge of the rafters rests against the Mauerlat or the upper crown of the frame.
The erection of a layered rafter system is allowed when the distance between the gables is not more than 6 m. For a greater distance, it is required to strengthen the system with vertical posts, with an emphasis on the bed, located on the upper part of the intermediate wall.
The figure below shows layered rafters: the structure and units that make up such a rafter system.
Hanging rafters rest against the "heels" in the puff. In the upper part, the rafter legs rest against each other. This design is a separate module in the shape of an isosceles triangle, which is called a truss truss among builders. This structure works on a spacer, but the tightening dampens this process, transferring a vertically directed load to the walls of the building.
Basic schemes and types of fastening of the hanging type truss system
There are many options for constructing a hanging rafter system, among which only three are most common:
- Triangular three-hinged. The structure of the rafters is a classic triangle, the upper sides of which are subjected to bending loads, the lower (tightening) dampens tension. To connect the elements of the unit, a frontal cut with a single or double tooth is used.

- Triangular three-pivot with a raised pull. This scheme is ideal if you need to create a residential attic. The raised tightening increases the tensile load of the rafter system, which ensures an even distribution of the load on the Mauerlats. The fastening of the tightening to the rafter leg is made by the "semi-rotary" cutting method.

- Triangular three-joint with a headstock and additional struts. This design is used to reduce the load on the deflection of the rafter.The tightening in such a system rests on the headstock collar, leveling the stretching due to the pulling down of the ridge knot, which, in turn, acts on the suspension, compressing the rafters.

Non-expansion and spacer rafter systems of the layered type
 Log cabins and log houses poorly tolerate loads acting on the expansion of the outer walls.
Log cabins and log houses poorly tolerate loads acting on the expansion of the outer walls.
In such cases, a spreader-free gable roof rafter system is practiced, which involves two points of support for each rafter leg:
- The lower part is beveled against the Mauerlat. The length of the bevel should not exceed the cross-section of the beam.
- The upper part rests on the ridge girder.
A feature of this design is the rigid fastening of the rafter legs to each other in the upper part. To attach the rafter leg to the Mauerlat, a movable connection method is used using a flexible steel plate.
When erecting a gable roof rafter system, spacer structures are also used, which are something in between, between hanging and layered rafters. The spacer fastening of the rafters of a gable roof suggests a change in the system of attaching the rafter legs to the Mauerlat from movable to rigid. Such schemes are used exclusively in houses with thick capital walls with a rigid Mauerlat mount. The rafters in this design rest against the walls with their lower parts, and against each other with the upper ones. The ridge girder is used, but does not play a significant role in the rigidity of the frame. To reduce the spacer loads, a scrum is included in the structure.
To increase the reliability of the roof frame, wind ties of the rafter roof are used, the task of which is to transfer wind loads to the load-bearing walls of the structure and to ensure the spatial rigidity of the roof. To create vertical wind ties of the rafter system, struts are installed at each rack. The lower part of these structural elements rests on a bench.
Rules for self-calculation of the rafter system

When self-calculating the rafter system, it is necessary to determine the correct cross-section of the beam based on the constant and temporary loads acting on it, including:
- A lot of materials for the roofing and rafter system.
- Wind pressure and precipitation.
Permanent loads include the weight of the battens and roofing. When choosing materials, it should be borne in mind that the pressure on the frame should not exceed 50 kg / m2... The snow load on the frame is equal to the weight of the snow multiplied by a coefficient that depends on the slope angle of the slopes.
The section of the rafter leg depends on the step. The smaller the distance between the rafters, the smaller the cross-section of the timber. For ease of understanding, it recommends that you familiarize yourself with the table of dependence of the length, step and section of the rafter legs.
The height of the ridge depends on the angle of inclination of the roof. The optimum angle for precipitation discharge is 35 - 45 °. In regions with strong wind loads, a roof slope angle of 20 to 45 ° is used.
When creating a gable roof rafter system, it is better to use dry coniferous timber of 1-3 categories. For bolts and ties used Pine or 1 grade larch. For rafters, Mauerlats, racks and girders, material of at least 2 grade is used. All other frame elements can be created from wood of 3 types.