Monolithic slab foundation: design features and installation principles
 Private developers, when choosing a foundation base for a house or outbuildings, prefer a tape structure as a reliable, economical and easy-to-use option. But in some cases, the only possible solution is the foundation of a monolithic slab. Such a foundation is required for construction on sandy soil, on hard and plastic loams, plastic clay. The design may also be in demand when erecting buildings on hard and plastic sandy loam, hard clay.
Private developers, when choosing a foundation base for a house or outbuildings, prefer a tape structure as a reliable, economical and easy-to-use option. But in some cases, the only possible solution is the foundation of a monolithic slab. Such a foundation is required for construction on sandy soil, on hard and plastic loams, plastic clay. The design may also be in demand when erecting buildings on hard and plastic sandy loam, hard clay.
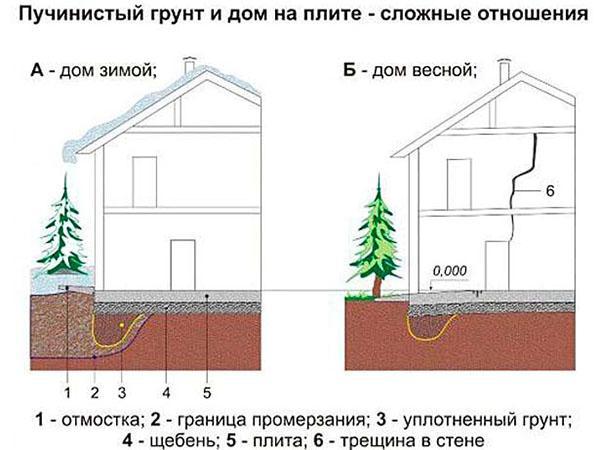
Features of the "pie" of the slab foundation
The slab-type foundation foundation does not require deepening - its ability to “float” and resist the forces of frost heaving is fully manifested precisely at the surface.
The basic version of the foundation pie is shown in the illustration: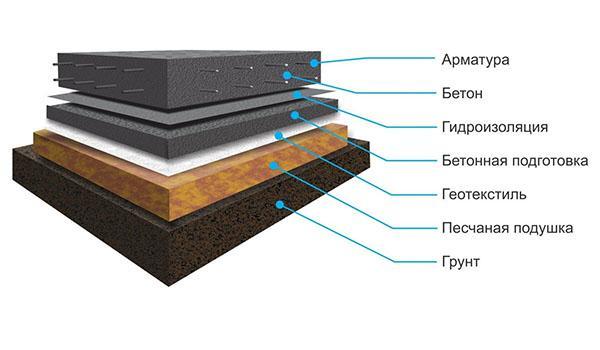
Foundation layers from bottom to top:
- Compacted soil - the bottom of a prepared pit.
- Pillow - made of sand or a mixture of sand with gravel, crushed stone. It is filled up in layers, leveled and rammed. The pillow dampens ground vibrations, reduces the intensity of the impact of loads from below on the foundation foundation.
- Geotextile. The dornite sheet protects the pillow from silting, reinforces it. Geotextiles can additionally be laid at the bottom of the pit, between layers of sand and rubble to increase the strength of the cake.
- The foundation. A thin leveling layer of concrete on top of the pillow helps to waterproof the foundation with high quality and correctly install the reinforcing frame.
- Waterproofing. Waterproof material protects the reinforced concrete foundation slab from moisture penetration from the ground. Waterproofing of a monolithic foundation slab is traditionally made of two or more layers of rolled bitumen material.
- Concrete slab. Actually, the foundation itself, the thickness of which depends on the magnitude of the loads on the foundation.
- Reinforcing frame. Reinforcement increases the strength of the monolithic structure, takes on tensile-compressive loads, preventing concrete cracking.
Varieties of slab foundation
 There are several options for the execution of the foundation slab. Most often it is a monolithic slab, the thickness of which is the same throughout the entire area. The advantages of such a base include ease of installation, the disadvantage is the close location of the upper edge to the ground surface - in this case, the base of the walls can be exposed to moisture, which harms the building structures.
There are several options for the execution of the foundation slab. Most often it is a monolithic slab, the thickness of which is the same throughout the entire area. The advantages of such a base include ease of installation, the disadvantage is the close location of the upper edge to the ground surface - in this case, the base of the walls can be exposed to moisture, which harms the building structures.
So that the edge of the slab is located higher above the surface of the soil, you should not increase its thickness - this will significantly affect the cost of the foundation. A more practical option would be to equip a slab with stiffeners.
Foundation monolithic slab with ribs up
 The monolithic structure is a flat base with reinforcing stiffeners protruding above the surface - it looks like a strip foundation on top of a slab. The ribs are placed around the perimeter and under the future load-bearing walls inside, if provided for by the project.
The monolithic structure is a flat base with reinforcing stiffeners protruding above the surface - it looks like a strip foundation on top of a slab. The ribs are placed around the perimeter and under the future load-bearing walls inside, if provided for by the project.
A foundation slab with upward stiffeners allows you to build a building with a basement or basement. In this case, the monolithic structure must be buried in the ground and the grillage ribs of a suitable height must be designed. Subsequently, a waterproofing layer is laid on top of the ribs and wall structures are mounted.
Slab foundation with ribs down
 To increase the bearing capacity of the slab foundation without deepening it, a monolithic structure is made with stiffening ribs directed downward.
To increase the bearing capacity of the slab foundation without deepening it, a monolithic structure is made with stiffening ribs directed downward.
There are two options for performing a monolithic slab with stiffening ribs down:
- Stiffeners are formed by trenches dug in the ground below the level of the reinforced concrete slab. A reinforcing frame is installed in the pit for the ribs, made as a whole with the frame of the slab itself, after which the concrete mixture is poured.
- A pit is being prepared with a flat bottom under the slab. A polymer slab insulation is laid on the waterproofed base - stiffeners will be formed in the intervals between the "islands" of the heat insulator and the walls of the pit. Before pouring the concrete mixture, the reinforcement cage is mounted.
Stiffeners should be located under the load-bearing walls and internal bulkheads. If the project does not provide for partitions, but it is necessary to increase the rigidity of the slab, the downward-facing ribs should be parallel to the short side of the building in increments of up to 3 meters.
 Laying a heat insulator, including extruded polystyrene foam under the foundation slab, not only allows you to equip stiffeners of the required dimensions, but also contributes to the insulation of the foundation base, and reduces the cost of heating the house. This type of foundation is called "Swedish slab". It is often supplemented with a water heating circuit.
Laying a heat insulator, including extruded polystyrene foam under the foundation slab, not only allows you to equip stiffeners of the required dimensions, but also contributes to the insulation of the foundation base, and reduces the cost of heating the house. This type of foundation is called "Swedish slab". It is often supplemented with a water heating circuit.
Prefabricated slab base
 In some cases, a precast concrete base is used instead of a monolithic slab foundation. The finished structures are stacked close to each other. But this option can only be used on rocky soils that are not prone to heaving. In other cases, the base may deform over time under uneven heaving loads due to the lack of a rigid connection between the plates.
In some cases, a precast concrete base is used instead of a monolithic slab foundation. The finished structures are stacked close to each other. But this option can only be used on rocky soils that are not prone to heaving. In other cases, the base may deform over time under uneven heaving loads due to the lack of a rigid connection between the plates.
The base of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs is used only in the case of the construction of outbuildings, baths, small light houses. A screed is made over the laid slabs. The technology of assembling a prefabricated foundation requires the involvement of special equipment for transporting and laying slabs.
Calculation of the thickness of the slab and reinforcing frame
 When constructing a slab foundation with your own hands, it is important to correctly calculate the thickness of the slab. Too thin a base will not withstand loads. Pouring an overly thick slab will lead to unnecessary financial costs.
When constructing a slab foundation with your own hands, it is important to correctly calculate the thickness of the slab. Too thin a base will not withstand loads. Pouring an overly thick slab will lead to unnecessary financial costs.
Please note: each centimeter of slab thickness is 1 cubic meter of concrete per 10 sq. m area.
The calculation should be entrusted to professionals or use a special program. The value is calculated based on the type of soil and the loads on the foundation. Therefore, it is necessary to have geological survey data on the site and a ready-made construction project. The standard thickness of the slab foundation is 200-300 mm.
The reinforcing frame for slabs up to 150 mm thick is made of one layer of mesh, located along the central horizontal axis. For slabs 200-300 mm, two parallel layers of mesh are required, installed with a distance of 30-50 mm from the bottom and top of the future slab. The diameter of the reinforcement is 12-16 mm, the pitch of the rods is 200-300 mm.
Under the load-bearing walls, the pitch of the rods is reduced due to the more rarefied arrangement of the elements in the central part of the slab.
It is most convenient to calculate the number of reinforcing bars and clamps for their fastening using a specialized calculator.
DIY foundation slab: step by step instructions
The whole complex of works on arranging the slab base of a house or an outbuilding can be done on your own.
Preparatory stage
 The area for the foundation is cleared of debris, trees and shrubs, after which the marking of the future foundation pit is performed. It is important to ensure that the tensioned cords form right angles. For the accuracy of the geometry, check the coincidence of the lengths of the diagonals of the marked rectangular area.
The area for the foundation is cleared of debris, trees and shrubs, after which the marking of the future foundation pit is performed. It is important to ensure that the tensioned cords form right angles. For the accuracy of the geometry, check the coincidence of the lengths of the diagonals of the marked rectangular area.
On the marked area, it is required to dig a pit taking into account the thickness of the sand-crushed stone cushion, footing, waterproofing and the design value of the slab deepening.
It is required to remove a layer of fertile soil with vegetation from the building spot, the depth of the pit is calculated relative to the prepared surface.
The bottom of the pit must be flat and horizontal, the soil is carefully tamped. The technology of building a foundation-slab can provide for the use of geotextiles to create a barrier between the soil and the sand bed - in this case, the sand does not silt up and is not washed out when flood groundwater rises. Cloths of geotextiles are laid with an overlap of 30 cm and approaching the walls of the pit.
Pillow arrangement
 At the bottom of the pit, sand is evenly poured with a layer of 100-120 mm. Then it is moistened with water and compacted with a vibrating plate. Then, according to the same principle, the next layer of sand is poured and rammed. The total thickness of the cushion must be at least 200 mm.
At the bottom of the pit, sand is evenly poured with a layer of 100-120 mm. Then it is moistened with water and compacted with a vibrating plate. Then, according to the same principle, the next layer of sand is poured and rammed. The total thickness of the cushion must be at least 200 mm.
Common critical mistakes: using sand with an admixture of clay, unloading the entire volume of sand into a pit at once, followed by leveling.
The sand cushion is covered with a layer of gravel or crushed stone 120-150 mm thick. Geotextiles can be pre-laid so that the layers do not mix. A layer of gravel is necessary to exclude capillary suction of moisture from the soil.
At the stage of arranging the pillow, it is required to lay all communications that will be brought out vertically through the thickness of the foundation slab.
Waterproofing
 Formwork is mounted on the finished pillow along the contour of the future slab. For rigidity from the outside, the formwork is propped up with spacers. The structure must be airtight so that moisture does not leave the working mixture during concreting.
Formwork is mounted on the finished pillow along the contour of the future slab. For rigidity from the outside, the formwork is propped up with spacers. The structure must be airtight so that moisture does not leave the working mixture during concreting.
For reliable waterproofing of the foundation, it is recommended to perform concrete preparation - a thin layer of concrete is poured over the compacted rubble. Layer thickness 50-70 mm, concrete grade M-100.
After the foundation has dried, waterproofing is laid from a special polymer profile membrane or two or three layers of rolled bituminous material. The waterproofing should go to the walls of the formwork, the edges of the sheets are glued together with bituminous mastic or fused, heated by a burner.
Insulation of the foundation
 In regions with cold winters, the thermal insulation of the foundation slab is practiced when it comes to building a residential building, where it will serve as the base of the floor. Insulation under the foundation slab is laid in an even layer if it is designed flat. When arranging a slab with stiffeners directed downward. From the same insulation, sites are formed in the designed places.
In regions with cold winters, the thermal insulation of the foundation slab is practiced when it comes to building a residential building, where it will serve as the base of the floor. Insulation under the foundation slab is laid in an even layer if it is designed flat. When arranging a slab with stiffeners directed downward. From the same insulation, sites are formed in the designed places.
Reinforcement
 The installation of the reinforcement cage starts from the bottom mesh. To maintain the required clearance of 30 mm from the base, the reinforcement rods are placed on special plastic supports.
The installation of the reinforcement cage starts from the bottom mesh. To maintain the required clearance of 30 mm from the base, the reinforcement rods are placed on special plastic supports.
First of all, all the longitudinal rods are laid. Then the transverse ones are attached to them using wire twists or plastic clamps. Welding is not used - overheating of the metal at the attachment points weakens the structure.
To place the second tier of the lattice at the required height above the lower one, use spider stands (they are also "frogs") over the entire area (2 pieces per square meter) and U-shaped edge elements.
Concrete works
 The pouring of a monolithic foundation slab should be performed within one shift, otherwise it is impossible to achieve the required structural strength. Working mixture requirements:
The pouring of a monolithic foundation slab should be performed within one shift, otherwise it is impossible to achieve the required structural strength. Working mixture requirements:
- concrete grade M-300 (strength class B22.5);
- mobility P3;
- coefficient of water resistance W8 and more;
- frost resistance class F
It is necessary to provide for a convenient approach for the automatic mixer, to take care of a concrete pump or trays for feeding the working mixture into the formwork in advance.
The mortar fed into the formwork must be immediately evenly distributed over the entire plane. For compacting concrete, eliminating air bubbles, you cannot do without a deep vibrator. The surface is leveled with a rule or with a vibrating screed.
The foundation of a monolithic slab should be covered with plastic wrap to protect it from precipitation, debris and accidental damage. A day later, within 5-7 days, it is required to wet the concrete surface with water. This will prevent the top layer of the slab from drying out and cracking. After 10-15 days, the formwork can be removed - the concrete will have time to gain more than 50% strength. The construction of the walls is started no earlier than a month after pouring - the concrete must fully mature.
 Knowing how to make a foundation for a slab for a house, you can save a lot of money on the construction of a summer house or a country house, a garage. In order for the foundation foundation to serve for more than one decade, it is important to strictly observe the technology of work and use high-quality materials.
Knowing how to make a foundation for a slab for a house, you can save a lot of money on the construction of a summer house or a country house, a garage. In order for the foundation foundation to serve for more than one decade, it is important to strictly observe the technology of work and use high-quality materials.